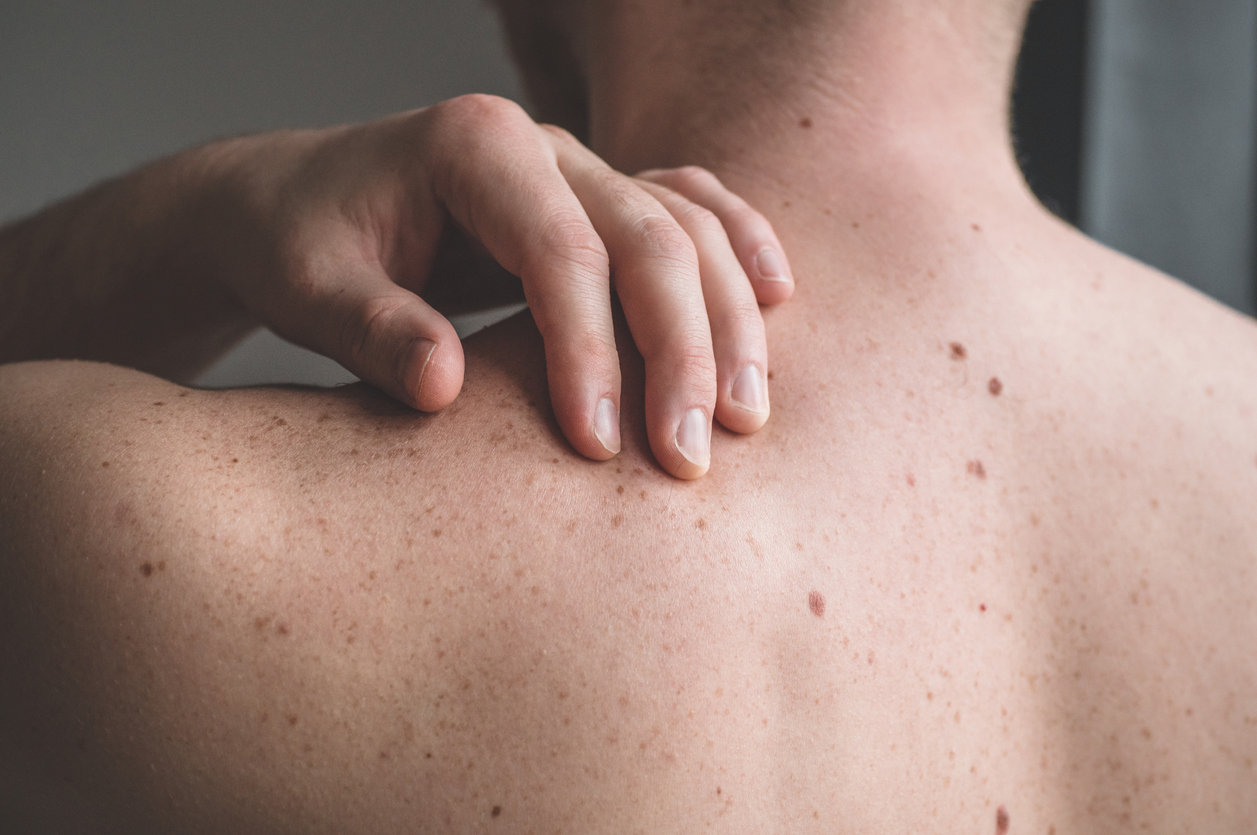
A skin biopsy is a procedure used to diagnose and treat various types of skin diseases. It involves taking a small sample of tissue from the affected area, which will then be examined under a microscope. This sample can help determine if a person has a specific type of infection, such as an allergic reaction or cancer. While it may sound intimidating, it is usually a relatively simple and quick procedure.
What is a Skin Biopsy?
A skin biopsy is a procedure used to collect cells from the skin. During a skin biopsy, a small tissue sample is removed from an area of the skin and examined in more detail under a microscope to help diagnose certain conditions or diseases. Skin biopsies can be performed on any body area and are sometimes referred to as skin incisions or punch biopsies.
What Does a Skin Biopsy Diagnose?
Skin biopsies can diagnose a wide range of skin conditions and diseases, such as skin cancer (melanoma or non-melanoma), psoriasis, eczema, warts, moles, and other growths. The biopsy can also help to confirm or exclude the diagnosis of certain inflammatory conditions that appear on the skin, such as lupus and scleroderma.
Skin Biopsy Preparation
Before a skin biopsy, it is important to get all the necessary information from your doctor, such as the location of the biopsy and any other instructions. You should also make sure you understand what will happen during the procedure so there are no surprises. You may also need to take a few steps to prepare for your skin biopsy. This includes avoiding any medications or products that can interfere with the biopsy. Your doctor may also ask you to stop using any topical creams on the area for a few days before the procedure.
How Does a Dermatologist Do a Skin Biopsy?
Before the procedure, your dermatologist will examine the skin and determine which type of biopsy is necessary. The type of biopsy performed will depend on the size and depth of the tissue sample being taken. Shave biopsies are generally used to remove superficial layers of skin, while punch biopsies remove deeper layers down to where fat begins.
Your dermatologist will administer a local anesthetic to numb the area before performing the biopsy. After this, they will use a scalpel to make an incision into the skin and remove cells from the affected area. The sample is then sent to a laboratory where it is analyzed under a microscope.
Do Skin Biopsies Hurt?
Skin biopsies are typically not painful, as the area is numbed with a local anesthetic before the procedure begins. However, most patients do report some discomfort or pressure during and after the procedure. Afterward, you may experience some mild swelling and redness around the site of the biopsy. These symptoms should gradually diminish in a few days.
What Happens After a Skin Biopsy?
Your dermatologist will discuss the results of the biopsy with you after they have been reviewed by a pathologist. Depending on the results, your doctor may recommend additional tests or treatments to address the condition that was diagnosed. It is important to follow all instructions given by your dermatologist and to attend all follow-up appointments to ensure that your skin remains healthy.
How Long Should You Keep a Skin Biopsy Covered?
After a skin biopsy, it is important to keep the area clean and covered. Your dermatologist will recommend how long you should cover the biopsy site, but it is usually between 3-7 days. During this time, you should also avoid activities that could put pressure on the area or increase your risk of infection.
Dermatology Evaluations at the Center for Derm
At the Center for Derm, we provide comprehensive dermatology evaluations and treatments. We strive to make sure that each patient receives the highest quality care possible. Our team of experienced physicians is committed to helping you understand any skin conditions you may have and providing you with effective solutions to address them. Contact us today to schedule an appointment.